Cohen Kappa¶
Module Interface¶
CohenKappa¶
- class torchmetrics.CohenKappa(task: Literal['binary', 'multiclass'], threshold: float = 0.5, num_classes: Optional[int] = None, weights: Optional[Literal['linear', 'quadratic', 'none']] = None, ignore_index: Optional[int] = None, validate_args: bool = True, **kwargs: Any)[source]
Calculates Cohen’s kappa score that measures inter-annotator agreement. It is defined as.
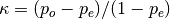
where
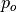 is the empirical probability of agreement and
is the empirical probability of agreement and 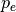 is
the expected agreement when both annotators assign labels randomly. Note that
is
the expected agreement when both annotators assign labels randomly. Note that
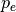 is estimated using a per-annotator empirical prior over the
class labels.
is estimated using a per-annotator empirical prior over the
class labels.This function is a simple wrapper to get the task specific versions of this metric, which is done by setting the
taskargument to either'binary'or'multiclass'. See the documentation ofBinaryCohenKappaandMulticlassCohenKappafor the specific details of each argument influence and examples.- Legacy Example:
>>> target = torch.tensor([1, 1, 0, 0]) >>> preds = torch.tensor([0, 1, 0, 0]) >>> cohenkappa = CohenKappa(task="multiclass", num_classes=2) >>> cohenkappa(preds, target) tensor(0.5000)
BinaryCohenKappa¶
- class torchmetrics.classification.BinaryCohenKappa(threshold=0.5, ignore_index=None, weights=None, validate_args=True, **kwargs)[source]
Calculates Cohen’s kappa score that measures inter-annotator agreement for binary tasks. It is defined as.
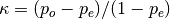
where
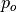 is the empirical probability of agreement and
is the empirical probability of agreement and 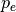 is
the expected agreement when both annotators assign labels randomly. Note that
is
the expected agreement when both annotators assign labels randomly. Note that
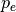 is estimated using a per-annotator empirical prior over the
class labels.
is estimated using a per-annotator empirical prior over the
class labels.Accepts the following input tensors:
preds(int or float tensor):(N, ...). If preds is a floating point tensor with values outside [0,1] range we consider the input to be logits and will auto apply sigmoid per element. Addtionally, we convert to int tensor with thresholding using the value inthreshold.target(int tensor):(N, ...)
Additional dimension
...will be flattened into the batch dimension.- Parameters
threshold¶ (
float) – Threshold for transforming probability to binary (0,1) predictionsignore_index¶ (
Optional[int]) – Specifies a target value that is ignored and does not contribute to the metric calculationweights¶ (
Optional[Literal[‘linear’, ‘quadratic’, ‘none’]]) –Weighting type to calculate the score. Choose from:
Noneor'none': no weighting'linear': linear weighting'quadratic': quadratic weighting
validate_args¶ (
bool) – bool indicating if input arguments and tensors should be validated for correctness. Set toFalsefor faster computations.kwargs¶ (
Any) – Additional keyword arguments, see Advanced metric settings for more info.
- Example (preds is int tensor):
>>> from torchmetrics.classification import BinaryCohenKappa >>> target = torch.tensor([1, 1, 0, 0]) >>> preds = torch.tensor([0, 1, 0, 0]) >>> metric = BinaryCohenKappa() >>> metric(preds, target) tensor(0.5000)
- Example (preds is float tensor):
>>> from torchmetrics.classification import BinaryCohenKappa >>> target = torch.tensor([1, 1, 0, 0]) >>> preds = torch.tensor([0.35, 0.85, 0.48, 0.01]) >>> metric = BinaryCohenKappa() >>> metric(preds, target) tensor(0.5000)
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
MulticlassCohenKappa¶
- class torchmetrics.classification.MulticlassCohenKappa(num_classes, ignore_index=None, weights=None, validate_args=True, **kwargs)[source]
Calculates Cohen’s kappa score that measures inter-annotator agreement for multiclass tasks. It is defined as.
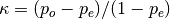
where
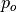 is the empirical probability of agreement and
is the empirical probability of agreement and 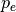 is
the expected agreement when both annotators assign labels randomly. Note that
is
the expected agreement when both annotators assign labels randomly. Note that
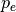 is estimated using a per-annotator empirical prior over the
class labels.
is estimated using a per-annotator empirical prior over the
class labels.Accepts the following input tensors:
preds:(N, ...)(int tensor) or(N, C, ..)(float tensor). If preds is a floating point we applytorch.argmaxalong theCdimension to automatically convert probabilities/logits into an int tensor.target(int tensor):(N, ...)
Additional dimension
...will be flattened into the batch dimension.- Parameters
num_classes¶ (
int) – Integer specifing the number of classesignore_index¶ (
Optional[int]) – Specifies a target value that is ignored and does not contribute to the metric calculationweights¶ (
Optional[Literal[‘linear’, ‘quadratic’, ‘none’]]) –Weighting type to calculate the score. Choose from:
Noneor'none': no weighting'linear': linear weighting'quadratic': quadratic weighting
validate_args¶ (
bool) – bool indicating if input arguments and tensors should be validated for correctness. Set toFalsefor faster computations.kwargs¶ (
Any) – Additional keyword arguments, see Advanced metric settings for more info.
- Example (pred is integer tensor):
>>> from torchmetrics.classification import MulticlassCohenKappa >>> target = torch.tensor([2, 1, 0, 0]) >>> preds = torch.tensor([2, 1, 0, 1]) >>> metric = MulticlassCohenKappa(num_classes=3) >>> metric(preds, target) tensor(0.6364)
- Example (pred is float tensor):
>>> from torchmetrics.classification import MulticlassCohenKappa >>> target = torch.tensor([2, 1, 0, 0]) >>> preds = torch.tensor([ ... [0.16, 0.26, 0.58], ... [0.22, 0.61, 0.17], ... [0.71, 0.09, 0.20], ... [0.05, 0.82, 0.13], ... ]) >>> metric = MulticlassCohenKappa(num_classes=3) >>> metric(preds, target) tensor(0.6364)
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
Functional Interface¶
cohen_kappa¶
- torchmetrics.functional.cohen_kappa(preds, target, task, threshold=0.5, num_classes=None, weights=None, ignore_index=None, validate_args=True)[source]
Calculates Cohen’s kappa score that measures inter-annotator agreement. It is defined as.
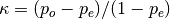
where
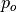 is the empirical probability of agreement and
is the empirical probability of agreement and 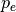 is
the expected agreement when both annotators assign labels randomly. Note that
is
the expected agreement when both annotators assign labels randomly. Note that
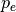 is estimated using a per-annotator empirical prior over the
class labels.
is estimated using a per-annotator empirical prior over the
class labels.This function is a simple wrapper to get the task specific versions of this metric, which is done by setting the
taskargument to either'binary'or'multiclass'. See the documentation ofbinary_cohen_kappa()andmulticlass_cohen_kappa()for the specific details of each argument influence and examples.- Legacy Example:
>>> target = torch.tensor([1, 1, 0, 0]) >>> preds = torch.tensor([0, 1, 0, 0]) >>> cohen_kappa(preds, target, task="multiclass", num_classes=2) tensor(0.5000)
- Return type
binary_cohen_kappa¶
- torchmetrics.functional.classification.binary_cohen_kappa(preds, target, threshold=0.5, weights=None, ignore_index=None, validate_args=True)[source]
Calculates Cohen’s kappa score that measures inter-annotator agreement for binary tasks. It is defined as.
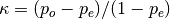
where
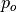 is the empirical probability of agreement and
is the empirical probability of agreement and 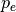 is
the expected agreement when both annotators assign labels randomly. Note that
is
the expected agreement when both annotators assign labels randomly. Note that
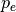 is estimated using a per-annotator empirical prior over the
class labels.
is estimated using a per-annotator empirical prior over the
class labels.Accepts the following input tensors:
preds(int or float tensor):(N, ...). If preds is a floating point tensor with values outside [0,1] range we consider the input to be logits and will auto apply sigmoid per element. Addtionally, we convert to int tensor with thresholding using the value inthreshold.target(int tensor):(N, ...)
Additional dimension
...will be flattened into the batch dimension.- Parameters
threshold¶ (
float) – Threshold for transforming probability to binary (0,1) predictionsweights¶ (
Optional[Literal[‘linear’, ‘quadratic’, ‘none’]]) –Weighting type to calculate the score. Choose from:
Noneor'none': no weighting'linear': linear weighting'quadratic': quadratic weighting
ignore_index¶ (
Optional[int]) – Specifies a target value that is ignored and does not contribute to the metric calculationvalidate_args¶ (
bool) – bool indicating if input arguments and tensors should be validated for correctness. Set toFalsefor faster computations.kwargs¶ – Additional keyword arguments, see Advanced metric settings for more info.
- Example (preds is int tensor):
>>> from torchmetrics.functional.classification import binary_cohen_kappa >>> target = torch.tensor([1, 1, 0, 0]) >>> preds = torch.tensor([0, 1, 0, 0]) >>> binary_cohen_kappa(preds, target) tensor(0.5000)
- Example (preds is float tensor):
>>> from torchmetrics.functional.classification import binary_cohen_kappa >>> target = torch.tensor([1, 1, 0, 0]) >>> preds = torch.tensor([0.35, 0.85, 0.48, 0.01]) >>> binary_cohen_kappa(preds, target) tensor(0.5000)
- Return type
multiclass_cohen_kappa¶
- torchmetrics.functional.classification.multiclass_cohen_kappa(preds, target, num_classes, weights=None, ignore_index=None, validate_args=True)[source]
Calculates Cohen’s kappa score that measures inter-annotator agreement for multiclass tasks. It is defined as.
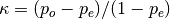
where
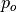 is the empirical probability of agreement and
is the empirical probability of agreement and 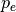 is
the expected agreement when both annotators assign labels randomly. Note that
is
the expected agreement when both annotators assign labels randomly. Note that
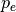 is estimated using a per-annotator empirical prior over the
class labels.
is estimated using a per-annotator empirical prior over the
class labels.Accepts the following input tensors:
preds:(N, ...)(int tensor) or(N, C, ..)(float tensor). If preds is a floating point we applytorch.argmaxalong theCdimension to automatically convert probabilities/logits into an int tensor.target(int tensor):(N, ...)
Additional dimension
...will be flattened into the batch dimension.- Parameters
num_classes¶ (
int) – Integer specifing the number of classesweights¶ (
Optional[Literal[‘linear’, ‘quadratic’, ‘none’]]) –Weighting type to calculate the score. Choose from:
Noneor'none': no weighting'linear': linear weighting'quadratic': quadratic weighting
ignore_index¶ (
Optional[int]) – Specifies a target value that is ignored and does not contribute to the metric calculationvalidate_args¶ (
bool) – bool indicating if input arguments and tensors should be validated for correctness. Set toFalsefor faster computations.kwargs¶ – Additional keyword arguments, see Advanced metric settings for more info.
- Example (pred is integer tensor):
>>> from torchmetrics.functional.classification import multiclass_cohen_kappa >>> target = torch.tensor([2, 1, 0, 0]) >>> preds = torch.tensor([2, 1, 0, 1]) >>> multiclass_cohen_kappa(preds, target, num_classes=3) tensor(0.6364)
- Example (pred is float tensor):
>>> from torchmetrics.functional.classification import multiclass_cohen_kappa >>> target = torch.tensor([2, 1, 0, 0]) >>> preds = torch.tensor([ ... [0.16, 0.26, 0.58], ... [0.22, 0.61, 0.17], ... [0.71, 0.09, 0.20], ... [0.05, 0.82, 0.13], ... ]) >>> multiclass_cohen_kappa(preds, target, num_classes=3) tensor(0.6364)
- Return type
