Cramer’s V¶
Module Interface¶
- class torchmetrics.CramersV(num_classes, bias_correction=True, nan_strategy='replace', nan_replace_value=0.0, **kwargs)[source]
Compute Cramer’s V statistic measuring the association between two categorical (nominal) data series.
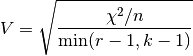
where
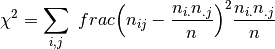
where
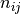 denotes the number of times the values
denotes the number of times the values 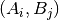 are observed with
are observed with 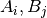 represent frequencies of values in
represent frequencies of values in predsandtarget, respectively.Cramer’s V is a symmetric coefficient, i.e.
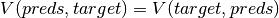 .
.The output values lies in [0, 1] with 1 meaning the perfect association.
- Parameters
num_classes¶ (
int) – Integer specifing the number of classesbias_correction¶ (
bool) – Indication of whether to use bias correction.nan_strategy¶ (
Literal[‘replace’, ‘drop’]) – Indication of whether to replace or dropNaNvaluesnan_replace_value¶ (
Union[int,float,None]) – Value to replaceNaN``s when ``nan_strategy = 'replace'kwargs¶ (
Any) – Additional keyword arguments, see Advanced metric settings for more info.
- Returns
Cramer’s V statistic
- Raises
ValueError – If nan_strategy is not one of ‘replace’ and ‘drop’
ValueError – If nan_strategy is equal to ‘replace’ and nan_replace_value is not an int or float
Example
>>> from torchmetrics import CramersV >>> _ = torch.manual_seed(42) >>> preds = torch.randint(0, 4, (100,)) >>> target = torch.round(preds + torch.randn(100)).clamp(0, 4) >>> cramers_v = CramersV(num_classes=5) >>> cramers_v(preds, target) tensor(0.5284)
Initializes internal Module state, shared by both nn.Module and ScriptModule.
- update(preds, target)[source]
Update state with predictions and targets.
- Parameters
- target: 1D or 2D tensor of categorical (nominal) data
1D shape: (batch_size,)
2D shape: (batch_size, num_classes)
- Return type
Functional Interface¶
- torchmetrics.functional.cramers_v(preds, target, bias_correction=True, nan_strategy='replace', nan_replace_value=0.0)[source]
Compute Cramer’s V statistic measuring the association between two categorical (nominal) data series.
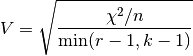
where
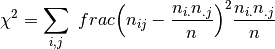
where
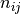 denotes the number of times the values
denotes the number of times the values 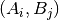 are observed with
are observed with 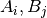 represent frequencies of values in
represent frequencies of values in predsandtarget, respectively.Cramer’s V is a symmetric coefficient, i.e.
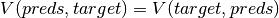 .
.The output values lies in [0, 1] with 1 meaning the perfect association.
- Parameters
preds¶ (
Tensor) – 1D or 2D tensor of categorical (nominal) data - 1D shape: (batch_size,) - 2D shape: (batch_size, num_classes)target¶ (
Tensor) – 1D or 2D tensor of categorical (nominal) data - 1D shape: (batch_size,) - 2D shape: (batch_size, num_classes)bias_correction¶ (
bool) – Indication of whether to use bias correction.nan_strategy¶ (
Literal[‘replace’, ‘drop’]) – Indication of whether to replace or dropNaNvaluesnan_replace_value¶ (
Union[int,float,None]) – Value to replaceNaN``s when ``nan_strategy = 'replace'
- Return type
- Returns
Cramer’s V statistic
Example
>>> from torchmetrics.functional import cramers_v >>> _ = torch.manual_seed(42) >>> preds = torch.randint(0, 4, (100,)) >>> target = torch.round(preds + torch.randn(100)).clamp(0, 4) >>> cramers_v(preds, target) tensor(0.5284)
cramers_v_matrix¶
- torchmetrics.functional.nominal.cramers_v_matrix(matrix, bias_correction=True, nan_strategy='replace', nan_replace_value=0.0)[source]
Compute Cramer’s V statistic between a set of multiple variables.
This can serve as a convenient tool to compute Cramer’s V statistic for analyses of correlation between categorical variables in your dataset.
- Parameters
matrix¶ (
Tensor) – A tensor of categorical (nominal) data, where: - rows represent a number of data points - columns represent a number of categorical (nominal) featuresbias_correction¶ (
bool) – Indication of whether to use bias correction.nan_strategy¶ (
Literal[‘replace’, ‘drop’]) – Indication of whether to replace or dropNaNvaluesnan_replace_value¶ (
Union[int,float,None]) – Value to replaceNaN``s when ``nan_strategy = 'replace'
- Return type
- Returns
Cramer’s V statistic for a dataset of categorical variables
Example
>>> from torchmetrics.functional.nominal import cramers_v_matrix >>> _ = torch.manual_seed(42) >>> matrix = torch.randint(0, 4, (200, 5)) >>> cramers_v_matrix(matrix) tensor([[1.0000, 0.0637, 0.0000, 0.0542, 0.1337], [0.0637, 1.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000], [0.0000, 0.0000, 1.0000, 0.0000, 0.0649], [0.0542, 0.0000, 0.0000, 1.0000, 0.1100], [0.1337, 0.0000, 0.0649, 0.1100, 1.0000]])
